Posted by Eduardo Munera
At this point, we are clear about what robot interoperability entails and the different levels of interoperability that can be distinguished. We are already convinced that it is all well and good, and we are ready to raise the flag of interoperability. The question is: Where do we start? Don't worry; throughout this article, we will address the most popular initiatives to standardize robot interoperability.

Open-RMF
Open-RMF (Robotics Middleware Framework) is an open-source platform aimed at enhancing interoperability and streamlining operations across diverse robotic platforms. Developed by leveraging ROS and supported by the Open Source Robotics Foundation, Open-RMF utilizes a modular design to ensure that robots of different types can work together seamlessly.
Open-RMF is designed as a modular software system that enables sharing and interoperability between multiple fleets of robots and physical infrastructure, such as doors, elevators, and building management systems. The offered solutions include a suite of management tools, such as web-based dashboards, a map and traffic editor, and adapters for integrating third-party APIs.
Scalability is another important feature of Open-RMF, enabling it to support a range of applications, from small setups to complex systems with many units, catering to various industry needs like healthcare and logistics.
Security and reliability are prioritized to protect data and communication, ensuring trust in automated operations. Furthermore, Open-RMF's extensibility through APIs and developer tools promotes innovation, allowing for the creation of customized applications and integrations.
In summary, Open-RMF is a groundbreaking solution in robotics middleware, equipped with the necessary features and tools to unlock the full potential of interoperable robotic systems.

VDA 5050
VDA 5050 is an open standard by the German Association of the Automotive Industry (VDA) aiming to standardize the communication between AGVs/AMRs and control software in the logistics and manufacturing sectors. This standard addresses a critical need within the automotive industry for interoperability and flexibility, as the rise of automation and robotics in production and logistics environments demands a unified approach to communication protocols.
The primary goal of VDA 5050 is to enable various robots, regardless of their manufacturer, to communicate effectively with a central control system. This standard encompasses multiple aspects of robot fleet operation, including task assignment, navigation control, status updates, and error handling. As of the date of this article, the latest specification of this protocol is version 2.0.0, and the message schemas are available as open-source for implementation.
By adopting VDA 5050, manufacturers and logistics providers can enhance the scalability, flexibility, and efficiency of their automated systems. This standard represents a significant step forward in creating more adaptive and integrated automated logistics solutions.
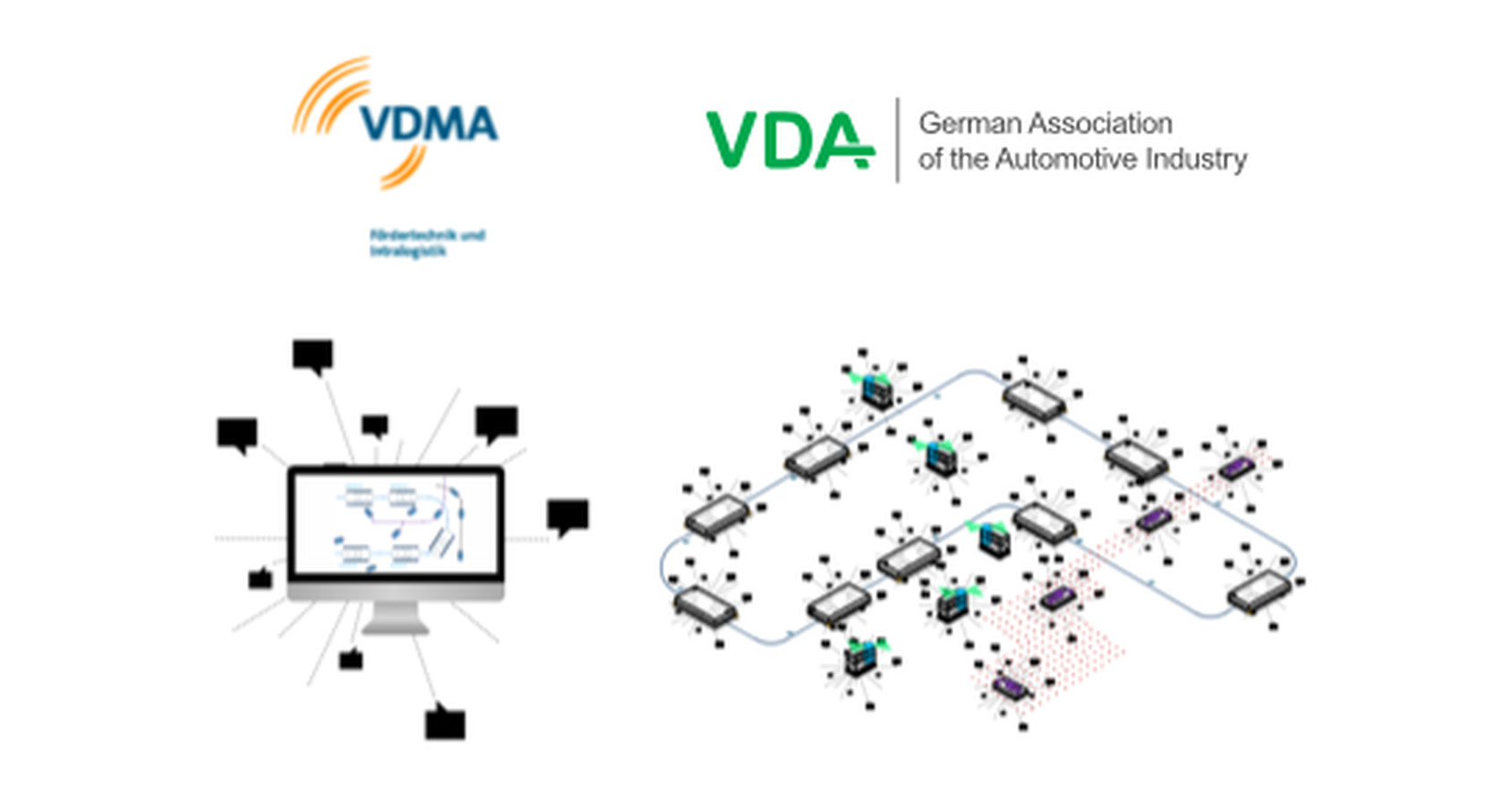
MassRobtics Interop
MassRobotics Interoperability Standard, is an innovative initiative aimed at enhancing the interoperability among robots, automated systems, and smart devices within the logistics, manufacturing, and broader industrial sectors. Developed by MassRobotics, a non-profit organization dedicated to supporting and promoting the robotics industry, this standard seeks to address a critical challenge in the robotics field: the seamless integration of diverse robotic systems and technologies.
The core objective of the MassRobotics Interop standard is to create a common framework that allows various robotic systems to communicate and work together more efficiently. This includes facilitating data exchange, coordinating actions between different robots and devices, and enabling a more cohesive operational environment. Such interoperability is vital for businesses looking to harness the full potential of robotics and automated technologies, as it can significantly reduce integration costs, enhance system flexibility, and improve overall operational efficiency.
By fostering an ecosystem where devices from different manufacturers can easily interact and share information, MassRobotics Interop aims to accelerate innovation, streamline operations, and promote the adoption of robotics across multiple industries. This standard represents a collaborative effort to build a more connected and dynamic future for robotics technology.

Other Initiatives
Worldwide, we are witnessing an increasing number of initiatives emerging in various countries. A notable example is the one put forward by the China Mobile Robot Industry Alliance (中国移动机器人产业联盟), a significant entity contributing to the advancement and standardization of the mobile robotics industry in China. The Alliance's proposed robotics standards are designed to meet the growing need for standardized practices, safety protocols, and interoperability among devices, which is becoming increasingly important.
Highlighting initiatives such as Open-RMF, VDA 5050, and MassRobotics, we observe a global movement towards robot interoperability, which is essential for the future of robotics. These efforts signal a shift towards standardization, scalability, and collaboration across the industry, encouraging the adoption of unified standards. By embracing these initiatives, the robotics industry is driving innovation and efficiency across various sectors, thus building a foundation for the next era of automated systems.